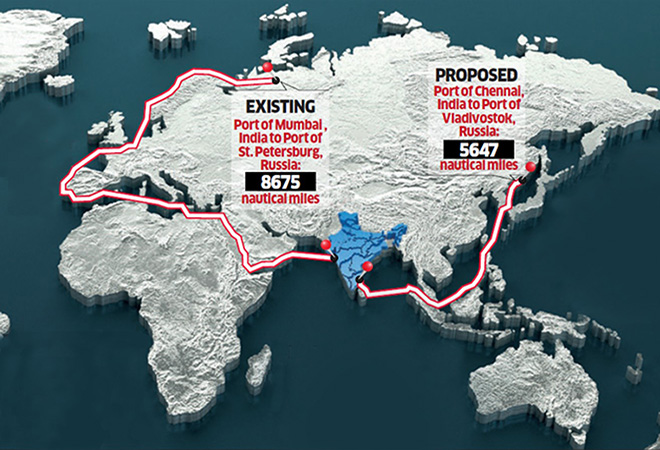
What is the Vladivostok to Chennai project?

The Chennai-Vladivostok Maritime Corridor is a significant project aimed at strengthening the economic ties between India and Russia by establishing a direct sea route between Chennai, India, and Vladivostok, Russia. Here’s an in-depth look at the project’s significance, potential impacts, and future prospects.
1. Overview of the Chennai-Vladivostok Project
The Chennai-Vladivostok Maritime Corridor, proposed as a direct sea route, would reduce shipping time from the traditional 40 days through the Suez Canal to just about 24 days, cutting logistical and operational costs. Initiated during the 2019 Eastern Economic Forum, this project was highlighted as a strategic effort to boost India-Russia trade relations and support energy and resource diversification. Vladivostok, being a central hub in the Russian Far East, holds untapped potential for cooperation in sectors like natural resources, defense, and technology.
2. Economic Significance
By establishing a streamlined route, India can access Russia’s energy resources and minerals more efficiently. This is especially significant in light of India’s growing energy demands. Moreover, Russia’s rich reserves of coal, oil, and natural gas, combined with metals like diamonds and gold, could help India diversify its import sources. For Russia, India presents a promising market, especially for oil and gas exports.
3. Strategic and Geopolitical Implications
The Chennai-Vladivostok Corridor would also play a significant role in shifting regional power dynamics by strengthening India’s trade alternatives. This project aligns with India’s Act East Policy, which focuses on deepening relationships with East Asian nations, and provides a counterbalance to China’s influence in the region, particularly along the Belt and Road Initiative (BRI).
The project has the potential to bring India into a stronger geopolitical alignment with countries in the Indo-Pacific region and allows for the exploration of cooperation with Japan and South Korea, who are also interested in the Russian Far East’s resources.
4. Potential Trade Boost
Currently, India’s trade with Russia stands at around $10-11 billion. The proposed corridor is anticipated to double or even triple this trade volume. The corridor will significantly simplify the export of key products, including pharmaceuticals, textiles, and agriculture from India to Russia, while improving imports of resources like hydrocarbons and timber from Russia. The ease of access could encourage a more balanced trade relationship, benefitting both countries economically.
5. Development of New Business Opportunities
The shorter transportation times and cost savings through this corridor are expected to attract Indian businesses to Russia’s Far East, especially in mining, agriculture, and forestry. India could also become a leading partner in Russia’s regional development, further opening avenues for investments and collaborations in infrastructure projects like roadways, railways, and ports in the Far East.
6. Impacts on the Shipping and Logistics Industry
The Chennai-Vladivostok Maritime Corridor will stimulate India’s shipping industry by creating new jobs and enhancing the competitiveness of Indian ports like Chennai. Streamlined logistics could also foster the growth of ancillary industries, including warehousing and distribution, and bring technological advancements to port management systems.
Russian and Indian logistics companies may also benefit, as a new, direct route reduces the risks associated with traditional shipping routes through the Strait of Malacca and the Suez Canal. This corridor will improve India’s position as a shipping and logistics hub in the Indo-Pacific, further strengthening its influence in the industry.
7. Environmental Benefits
Shorter shipping routes have environmental advantages. The reduction in travel time would decrease fuel consumption, thereby lowering greenhouse gas emissions. Both India and Russia have expressed interest in making this corridor environmentally sustainable, potentially investing in green technology for ships and ports.
8. Challenges to Implementation
Despite its potential, the Chennai-Vladivostok Corridor faces certain challenges:
- Infrastructure Gaps: Adequate port facilities and intermodal logistics systems are essential. Ports on both ends of the corridor will require significant upgrades to handle increased traffic efficiently.
- Legal and Regulatory Hurdles: Establishing common regulations for customs and trade policies could be complex and might require further negotiations between India and Russia.
- Financial Commitments: The project demands substantial investments from both governments. It’s likely that financial support will be sought from private investors or international development funds.
- Geopolitical Risks: As the corridor would position India and Russia as stronger partners in the region, potential diplomatic resistance from other major economies is a possibility.
9. Future Prospects
The Chennai-Vladivostok Maritime Corridor reflects a new chapter in India-Russia relations, with both countries committed to diversifying their economic ties. Success of the project could pave the way for similar regional trade corridors, connecting other Indian ports to those in the Russian Far East, thereby enhancing economic resilience for both countries.